A technical guide to setting up hardware vs. software RAID involves understanding their differences, preparation steps, configuration processes, and maintenance considerations.
Hardware RAID Setup:
-
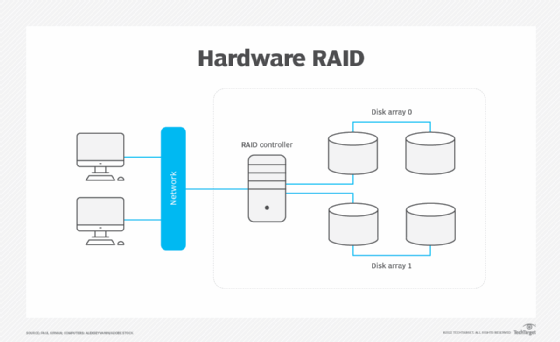
Definition: Uses a dedicated RAID controller card with its own processor and memory to manage RAID functions independently from the host CPU.
-
Preparation:
- Obtain a compatible hardware RAID controller card.
- Use identical drives (same make, model, capacity) for best performance and reliability.
- Ensure the server or PC supports the RAID controller hardware.
-
Configuration:
- Install the RAID controller card into the system.
- Connect the physical drives to the RAID controller.
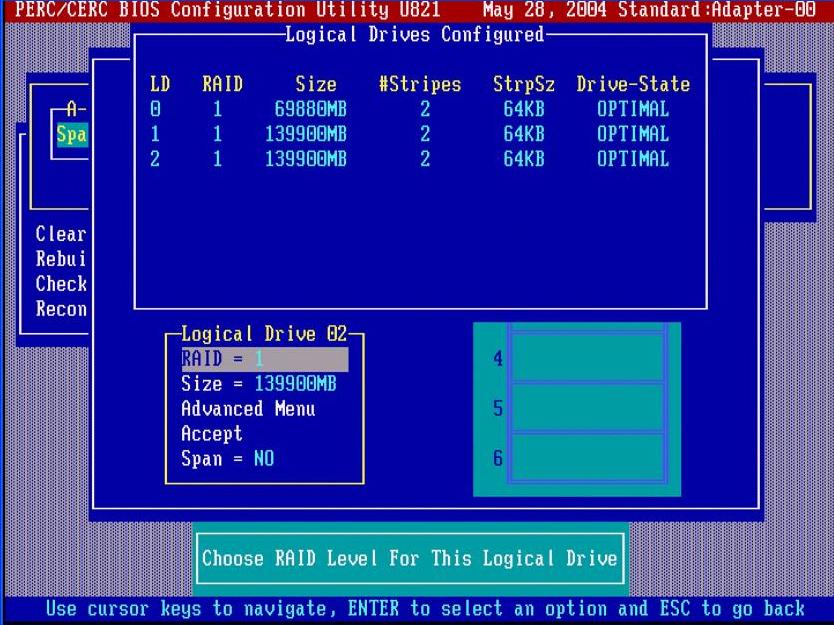
- During system boot, enter the RAID controller’s BIOS/firmware utility (usually via a key combination like Ctrl+R).
- Create the RAID array by selecting RAID level (e.g., RAID 0, 1, 5, 10) and assigning disks.
- Save configuration and exit.
- Install or boot the operating system; install RAID controller drivers if required.
- Use RAID management software provided by the controller vendor for monitoring and maintenance.
-
Advantages:
- Offloads RAID processing from CPU, improving performance especially in write-intensive tasks.
- Supports hot-swapping and advanced RAID levels.
- More reliable with better failure handling.
-
Considerations:
- Higher cost due to dedicated hardware.
- Configuration tied to the RAID controller; migrating arrays to different controllers can be complex.
Software RAID Setup:
-
Definition: RAID is managed by the operating system using software drivers without dedicated hardware.
-
Preparation:
- Use identical drives for optimal performance and reliability.
- Ensure the operating system supports software RAID (common in Windows, Linux, macOS, BSD variants).
-
Configuration:
- Connect physical drives directly to the motherboard or standard disk controllers.
- In the OS, use built-in utilities to create RAID arrays:
- Windows: Disk Management or Storage Spaces.
- Linux: mdadm tool.
- macOS: Disk Utility or command-line tools.
- Select RAID level and assign disks.
- Format and mount the RAID volume.
-
Advantages:
- Lower cost—no additional hardware required.
- Greater flexibility in RAID levels and reconfiguration.
- Easier to set up and manage within the OS environment.
-
Considerations:
- Uses host CPU for RAID operations, which can impact system performance under heavy I/O.
- RAID configuration is OS-dependent; migrating arrays between different OSes can be challenging.
- Limited support for hot-swapping and advanced RAID features.
Best Practices for Both:
- Use identical drives to avoid performance bottlenecks and compatibility issues.
- Maintain regular backups; RAID is not a substitute for data backup.
- Monitor drive and array health using appropriate tools to preempt failures.
- Choose RAID level based on needs: e.g., RAID 1 for redundancy, RAID 0 for performance, RAID 5/6 for a balance of both.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hardware RAID | Software RAID |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Dedicated RAID controller hardware | Managed by OS software |
| Performance | High; offloads CPU | Depends on host CPU; may reduce performance |
| Cost | Higher due to hardware | Lower; no extra hardware needed |
| Flexibility | Limited by controller compatibility | More flexible and easier to reconfigure |
| Reliability | More reliable with advanced failure handling | Dependent on OS; less robust |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited by OS and software |
| Hot-swapping support | Often supported | Rarely supported |
| OS Dependency | Less dependent | Highly dependent |
This guide provides a clear technical overview for setting up hardware vs. software RAID, helping users choose based on performance needs, budget, and system environment.


















WebSeoSG offers the highest quality website traffic services in Singapore. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 40 SGD per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation