Two‑Tower models (used mainly for retrieval/pre‑ranking) increase reach by enabling fast, scalable candidate generation over very large item sets, while multi‑stage ranking pipelines (recall → pre‑rank → rank → re‑rank) broaden and shape reach by combining high‑recall retrieval with progressively more precise relevance filters and business objectives.
Essential context and supporting details
-
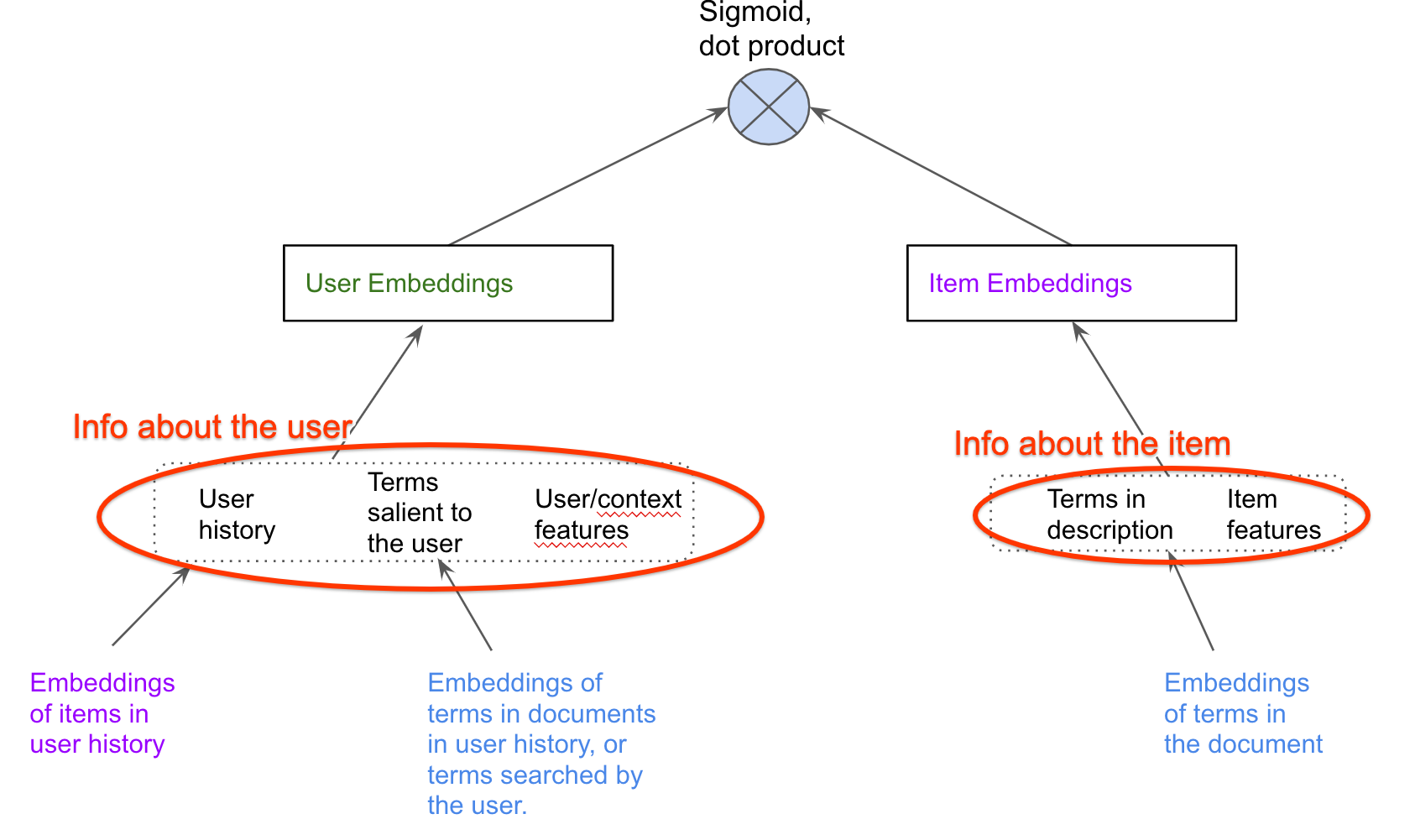
Two‑Tower model role and why it increases reach
- Two‑Tower learns separate embeddings for users and items and scores them via a fast similarity (dot product or cosine) so you can retrieve top‑K candidates from billions of items with ANN search, which directly expands the set of items considered for a request and thus improves raw reach.
- Because item embeddings are pre‑computed and user embeddings are computed online, inference cost is O(N + kM) for pre‑ranking (model inference + retrieving/scoring k candidates), keeping latency low while allowing many candidates to be considered.
- The architecture’s decoupling (user tower vs item tower) and use of ANN make it practical to add many items/features (e.g., contextual, numerical, NLP) without prohibitive online cost, further increasing reachable inventory.
-
How Two‑Tower interacts with multi‑stage ranking (effects on reach at each stage)
- Multi‑stage pipelines separate concerns: early stages prioritise recall and efficiency (retrieval, pre‑rank often Two‑Tower), later stages prioritise fine‑grained relevance and business goals (ranking, re‑ranking) using heavier models.
- The Two‑Tower pre‑rank stage supplies a broader candidate set (higher recall) to downstream rankers, so any improvements to Two‑Tower recall directly lift the initial reach available to ranking stages.
- Later ranking stages narrow that set based on stronger interaction modelling and business objectives; if pre‑rank reach is too narrow or biased, downstream stages can never show items that were never retrieved—so Two‑Tower design determines the ceiling of possible reach.
-
Trade‑offs that influence final reach and quality
- Efficiency vs interaction modelling: Two‑Tower scales but models limited cross features/interactions; richer interactions are deferred to expensive rankers, meaning Two‑Tower may miss items that require fine‑grained feature interactions unless mitigations are used (e.g., multi‑head embeddings, attention variants).
- Diversity vs relevance: ANN retrieval and embedding loss functions tuned for click probability can bias toward popular or similar items, reducing catalogue diversity and long‑tail reach unless explicit training/serving techniques (diversity-aware loss, multi‑objective towers, candidate expansion) are applied.
- Storage and latency constraints: approaches that increase per‑item representation (multi‑head/item heads) or more complex output interactions increase storage and inference cost and can reduce feasible candidate set size in real time, thus reducing effective reach if not engineered carefully.
-
Engineering and modelling levers to increase reach while maintaining relevance
- Improve Two‑Tower recall: richer features, sequential/contextual towers (sequence-aware embeddings), or multi‑head representations raise the chance of retrieving relevant long‑tail items.
- Use diversified retrieval: combine multiple retrieval sources (content, collaborative, popularity, user‑segment) so the Two‑Tower’s ANN is only one recall signal among many to increase coverage.
- Multi‑objective training: optimise embedding loss for both relevance and diversity or multiple business metrics so retrieved candidates better match downstream goals.
- Hybrid architectures: augment Two‑Tower with light-weight cross features or cheap interaction modules at pre‑rank to catch items needing some interaction signal without full ranking cost.
- Sampling and re‑scoring strategies: retrieve a larger candidate pool (bigger K) and let the ranking stage re‑score/penalise irrelevant items, trading extra downstream cost for higher potential reach.
-
Practical impacts observed in industry (examples)
- Companies use Two‑Tower for large‑scale retrieval to replace many specialised models and expand coverage while saving compute (Uber’s unified Two‑Tower replaced many city models and allowed more features to be added).
- Instagram/Spotlight/other systems rely on two‑tower retrieval for scalable candidate generation, then use heavier rankers to refine results—this separation enables both wide reach and high final relevance when engineered well.
When Two‑Tower harms reach (common failure modes)
- Overfitting to popular signals or embedding collapse can concentrate retrieval on a small set of items, reducing long‑tail reach.
- Too small K or tight latency budgets force aggressive pre‑rank pruning so many potentially relevant items never reach the ranker.
- Using only a single retrieval method (only Two‑Tower ANN) without other recall sources leaves blind spots for items better surfaced by content or graph signals.
If you want, I can:
- Sketch a concrete evaluation plan (metrics and offline/online experiments) to measure how Two‑Tower changes reach for your system.
- Propose specific model or pipeline changes (loss functions, multi‑head embeddings, candidate expansion strategies) tailored to your constraints (latency, storage, traffic).



















WebSeoSG offers the highest quality website traffic services in Singapore. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 40 SGD per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation