Here is an explanation of the common RAID levels 0, 1, 5, 6, and 10, highlighting their key features, advantages, and disadvantages:
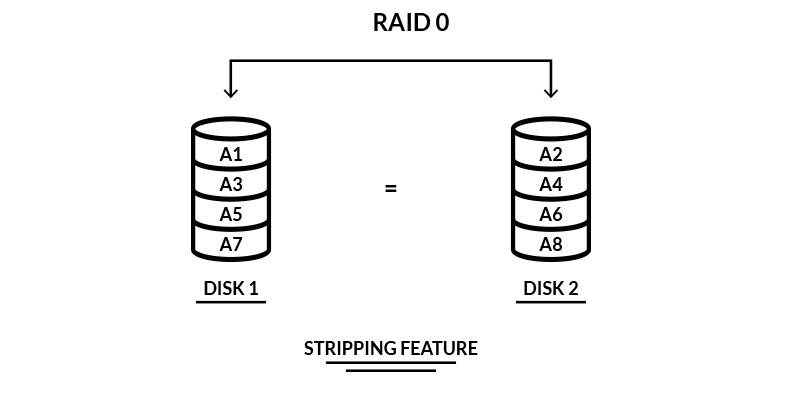
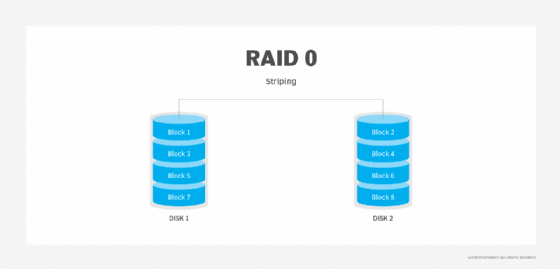
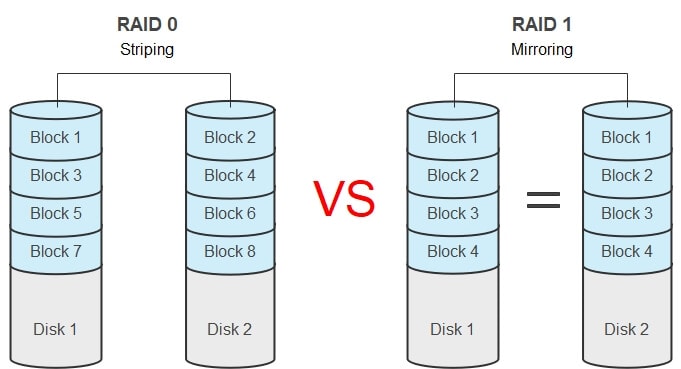
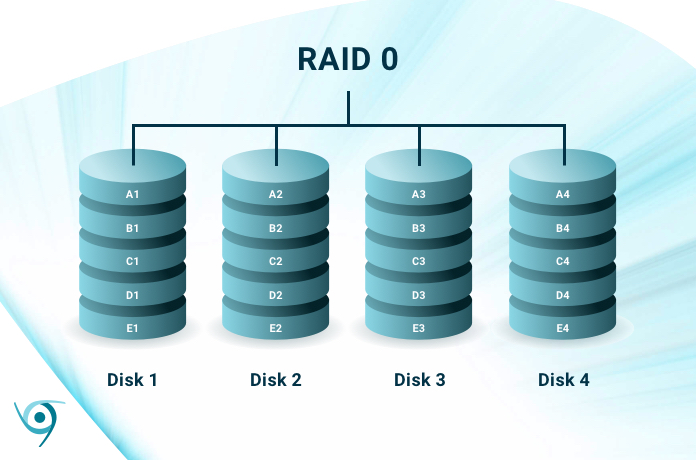
RAID 0 (Striping)
- Requires a minimum of 2 disks.
- Data is split into blocks and striped across all disks, improving read/write performance significantly.
- No redundancy or fault tolerance; if one disk fails, all data is lost.
- Total storage capacity is the sum of all disks.
- Best suited for non-critical systems where speed is the priority.
RAID 1 (Mirroring)
- Requires a minimum of 2 disks.
- Data is duplicated (mirrored) exactly on two or more disks.
- Provides excellent fault tolerance; if one disk fails, data is still available on the other.
- Storage capacity is effectively halved because data is duplicated.
- Performance for reads can improve, but writes are slower due to duplication.
RAID 5 (Striping with Distributed Parity)
- Requires a minimum of 3 disks.
- Data and parity (error correction information) are striped across all disks.
- Can tolerate the failure of one disk without data loss.
- Provides a good balance of performance, storage efficiency, and fault tolerance.
- Write performance is slower than RAID 0 due to parity calculations.
RAID 6 (Striping with Double Distributed Parity)
- Requires a minimum of 4 disks.
- Similar to RAID 5 but with two sets of parity information.
- Can tolerate failure of two disks simultaneously.
- Offers higher fault tolerance than RAID 5 but with additional overhead on write performance.
- Suitable for critical systems requiring high availability.
RAID 10 (RAID 1+0, Mirroring + Striping)
- Requires a minimum of 4 disks.
- Combines RAID 1 and RAID 0 by first mirroring data and then striping across mirrored sets.
- Provides both high performance and fault tolerance.
- Can tolerate multiple disk failures as long as no mirrored pair is completely lost.
- More expensive in terms of storage efficiency since half the capacity is used for mirroring.
| RAID Level | Minimum Disks | Fault Tolerance | Performance | Storage Efficiency | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 0 | 2 | None | High | 100% | High-speed, non-critical storage |
| RAID 1 | 2 | 1 disk | Moderate | 50% | Critical data needing redundancy |
| RAID 5 | 3 | 1 disk | Good | (N-1)/N | Balanced performance & redundancy |
| RAID 6 | 4 | 2 disks | Moderate | (N-2)/N | High fault tolerance |
| RAID 10 | 4 | Multiple disks | High | 50% | High performance + redundancy |
This summary should help you understand the trade-offs between speed, redundancy, and storage efficiency for each RAID level. RAID 0 maximizes speed but has no fault tolerance, RAID 1 focuses on redundancy, RAID 5 and 6 add parity-based fault tolerance with varying levels of protection, and RAID 10 combines mirroring and striping for both speed and redundancy.


-660.jpg)













WebSeoSG offers the highest quality website traffic services in Singapore. We provide a variety of traffic services for our clients, including website traffic, desktop traffic, mobile traffic, Google traffic, search traffic, eCommerce traffic, YouTube traffic, and TikTok traffic. Our website boasts a 100% customer satisfaction rate, so you can confidently purchase large amounts of SEO traffic online. For just 40 SGD per month, you can immediately increase website traffic, improve SEO performance, and boost sales!
Having trouble choosing a traffic package? Contact us, and our staff will assist you.
Free consultation